The process of neutralisation is accompanied by the evolution of heat.The amount of heat evolved when one gram equivalent of an acid is neutralised by one gram equivalent of a base is known as heat of neutralisation.
Apparatus Required:
Ostwald calorimeter ,N/5 HCl,N/5NaOH solution, Beckmann thermometer, distilled water.
Procedure:
The calorimeter of known water equivalent,W gram (say),stirrer are thoroughly washed and dried.200 ml of an exactly,0.2 N sodium hydroxide solution is pipetted out into the calorimeter and then placed inside the enclosure . All the rest process should be according to theory of the following image.
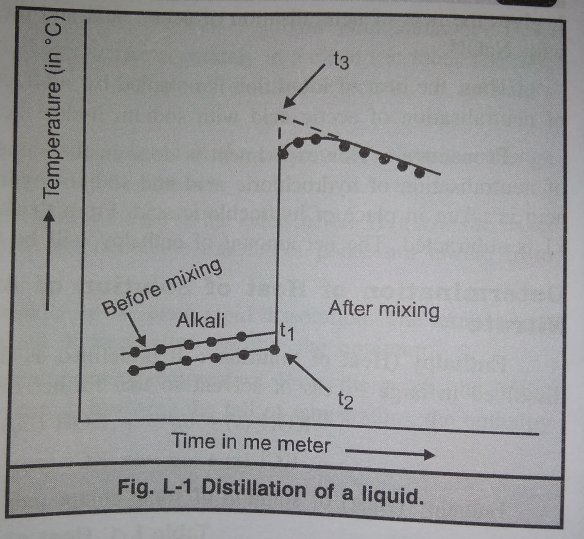
And the image shows the graph showing distillation of a liquid.
Calculation:
- Water equivalent of the calorimeter = Mass × specific heat=W gram.
- Initial temperature of alkali ( from graph)= t1°c
- Initial temperature of the acid=t2°c
- Total amount of heat produced= Q Cal.
- Heat of neutralisation of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide = 20Q Cal.

